To President-elect Donald Trump, “tariff” is the most beautiful word in the dictionary. His campaign-trail proposals included a 60 per cent duty on Chinese goods and 20 per cent on European ones. All things being equal, higher duties should translate into less trade. Isn’t that bad for shipping? Maersk shareholders think not.
The 15 per cent rise in the Danish freight company’s stock over the past month suggests hope that — at least in the short term — Trump’s tariffs won’t entirely snarl up the shipping market. The US is a sizeable, rather than giant, tassel in the global trade tapestry. In tonnes, it accounts for 5 per cent of global seaborne imports, according to Clarksons, a shipping service provider. Bilateral US-China trade accounts for 1.4 per cent of global seaborne goods transport.
Tariffs could even raise US imports, at first. A surge looks inevitable, as importers seek to stockpile goods ahead of the duties kicking in. Even thereafter, consumers may swallow higher prices to a degree, and companies settle for lower margins.
Where stuff just gets too expensive, other imports could take up the slack. A harder bludgeon for Chinese-made products would leave European companies at a relative advantage in the US market. And even where locally-produced goods shake out ahead, it would take US companies some time to increase their production capacities.
The impact of a near-term surge in shipping demand would be amplified by the stretched state of the shipping market. Disruption in the Red Sea has lengthened journeys, and while freight rates are off their peak, the Shanghai Containerized Freight Rate is still more than twice as high as it was in 2023.
By way of history, Trump’s last experiment with tariffs ended up clipping global seaborne trade — measured in tonnes/km — by only 0.5 per cent. Trouble is, such calculations only stack up if global growth holds up, and trade mostly moves around to adjust to tariffs. But trade wars have a habit of escalating as recipients slap on tariffs of their own. Over time, that would sink global GDP, and shipping demand with it.
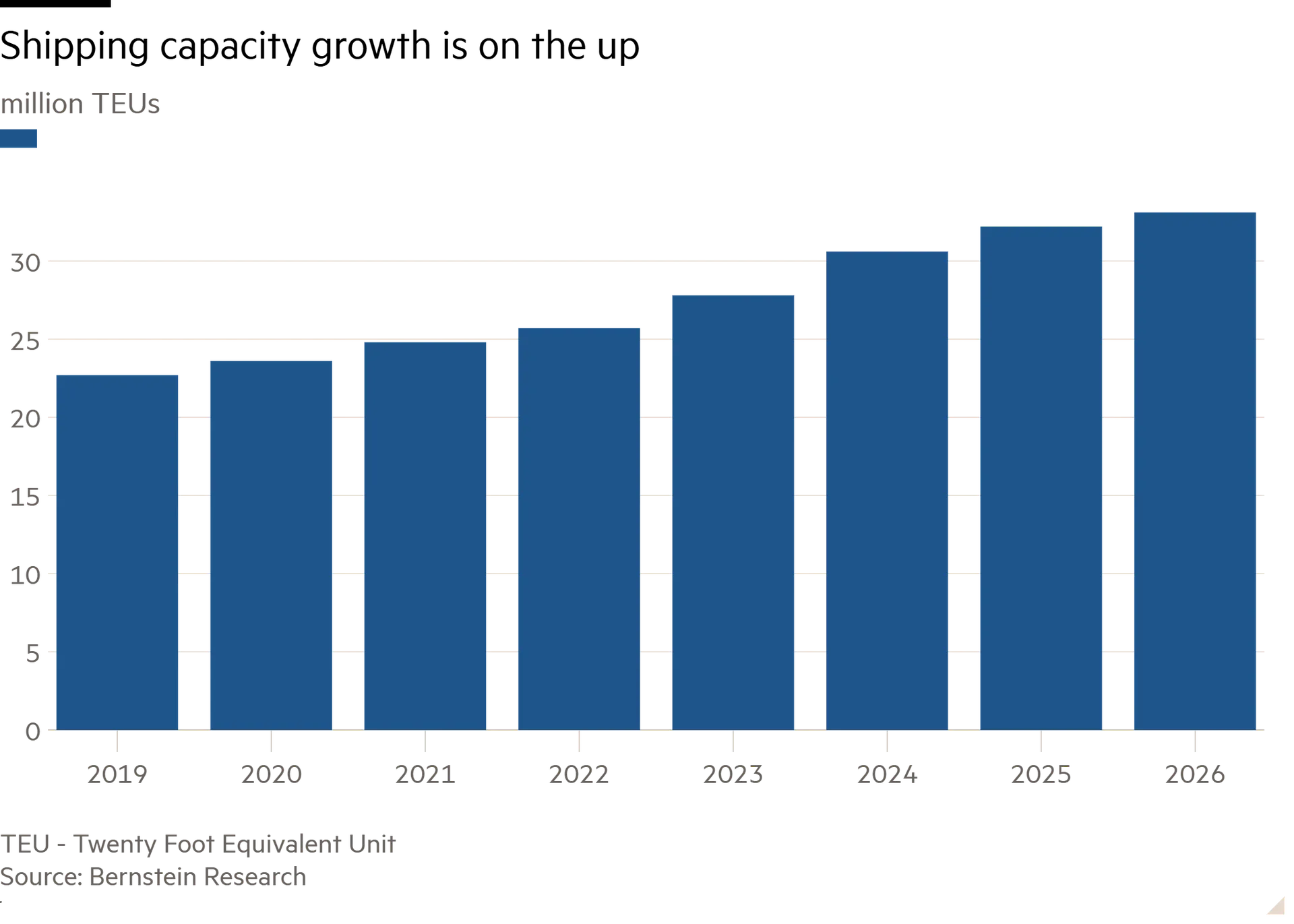
That’s particularly worrying given the sector spent its Covid-era bonanza on new ships. Next year’s fleet is set to be more than 40 per cent larger than that in 2019, according to Bernstein. The combination of looming risks to global growth and shipping overcapacity would certainly make for choppy waters.
The path from campaign pronouncement to actual policy is unclear, so it is hard to estimate with accuracy the size and shape of disruption to global trade. Investors are for now betting that it is nothing shipping companies like Maersk cannot navigate around.