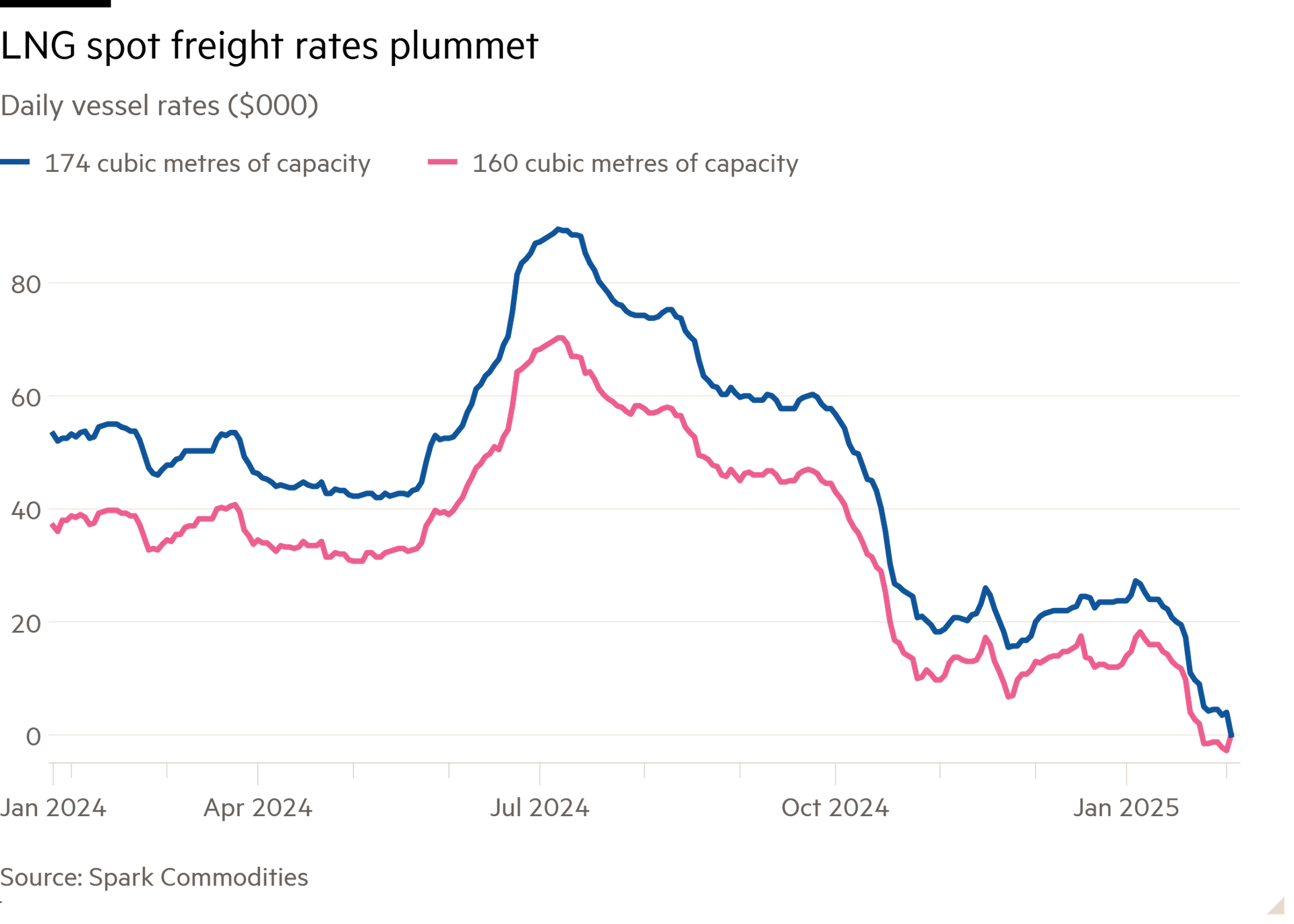
It is a rum old business when you cannot cover your costs. Just ask the owners of vessels ferrying liquefied natural gas across the seas. Spot charter rates in the Atlantic have plummeted more than 90 per cent since November to $4,000 a day, causing them to spring a leak.
An expected boom in LNG — driven by Europe’s pivot away from Russian gas and gung-ho US projects — has unleashed a flurry of shipbuilding. Yet the global supply of the liquid fuel grew just 2.5 per cent last year, a fraction of typical annual average growth in recent years. The extra 10bn cubic metres was less than one-third of the extra seaborne capacity.
The resulting losses are painful for ship operators, but not permanent. Manufacturing ships is an up-and-down game. Vessels take time to build; just not quite so long, it transpires, as it takes to get LNG plants online.
Messy politics, insurgencies and funding uncertainty add to the practicalities of building plants in the US, Africa and elsewhere; France’s TotalEnergies last month announced further delays to its $20bn project in Mozambique, launched in 2020.
Worse, price differentials between the European and Asian markets have made it more profitable for the US, the biggest exporter, to ship LNG to Europe rather than Asia. That is a shorter trip, meaning still greater availability of ship hours. China’s retaliatory sanctions on US LNG may — at the margin — further curtail the average length of trips.
For plenty of ship owners, this is water off a duck’s back: charter rates are set in advance and only a minority are struck at the spot rate. Besides, they know it is a question of when, not if, the cycle turns. Expect an improvement in the imbalance this year rather than a complete reversal.
Yes, LNG supply will grow; the International Energy Agency is forecasting 5 per cent in 2025. Europe, which is under regulatory orders to fill 90 per cent of gas storage facilities by November this year, needs to stock up. As of now, levels are running at about 53 per cent.
All that should be sufficient to nudge rates up from the seabed, even given increased shipping capacity and lacklustre growth from China. The world’s biggest LNG buyer is having a relatively mild winter and its slower economic growth does not tally with a big jump in energy consumption.
Further ahead, weather permitting, the outlook improves further. Shell of the UK is reckoning on a 50 per cent increase in LNG demand from 2023 to 2040. More projects should be coming online. Once again, traders will be griping about the cost of delivery.